According to a wpi pdf on "The Emerging Role of Robotics in Personal Health Care", the definition of a robot is composed of three things: actuate, sense and process. " a robot is a machine that is capable of obtaining data from its environment by means of sensors, processing the data at least to some extent, and reacting to this data by means of actuators."(pg 41)
In the research pdf, they also mentioned several focus areas of current technology and ongoing research in robotics within the health care industry. (pg 42-52)
Motivation of Health Care Industry
- There are various reasons why health care has turned to robotics, such as an increasing
elderly population, worker shortages, and increasing health care expenditures. - Robotics technologies have been remarkably developed in numerous industries such as nuclear power, military, medicine, and health care. These innovations in robotics significantly improved the health care industry and made it much more accessible to the general public. The progress of robotics in healthcare is driven by the health care needs of our society. The overall quality of health care has increases as the technology associated with it develops. As the quality of health care technology improves, the applications of the technology become much more specific, and this results in more specific fields of health care robotics
Clinical Applications.
- Surgical robots have become extremely sophisticated, even allowing surgeons to operate them from thousands of miles away. The da Vinci surgical robot system is a good example of the progress surgical robotics has made since its conception.
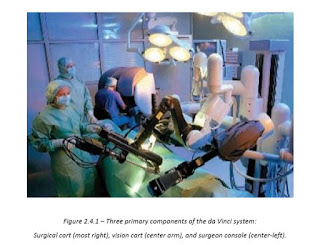
- da Vinci System
- One of the most well-known surgical robots, the da Vinci robot. More than 800 hospitals in the United States and Europe use the robot in various types of surgery. This system is undergoing considerable research and has been successfully applied in general surgery, cardiothoracic surgery, urology, gynecology, and possibly otolaryngology. The da Vinci system is made up of three primary components (many other applications can be added on): a surgical cart, vision cart, and surgeon console.
- Description about the figure "da Vinci Surgical System" (pg 44):
- The surgical cart is a robotic manipulator with three arms: one camera arm with a 12mm stereoscopic laparoscope and two others arms that hold 8mm instruments. One interesting technology applied here is the EndoWrist Instruments technology. Tiny computer-enhanced mechanical wrists allow a full 7 degrees of freedom at the instrument tips. Instrument tips are aligned with the instrument controllers electronically to provide optimal hand-eye orientation and natural operative capability.
- This innovative wrist was inspired from the Black Falcon of MIT. Overall visualization of operation is performed by the vision cart, which consist of two three-chip cameras mounted within one integrated and three dimensional 12mm stereo endoscope with two separate optical channels. The operative images are transmitted to a high-resolution binocular display at the surgeon console. The surgeon can see the operation in a 3-D (can be changed into 2-D) stereoscopic illustration on the console. Then he maneuvers robotic manipulators, which allow him to control the robotic arms and cameras.
- This setup achieves more precise and accurate manipulations of instruments than those that can be achieved from conventional endoscopic surgery
- da Vinci Surgical System - Peeling A Grape
- Here are some of Mayo Clinic's views of the Da Vinci System in the article "Robots/Robotics in Healthcare":
- Advantages:
- More controlled, controllable, and thus, potentially safer environment for both the patient and physician, increased precision of surgical manipulation, improved vision due to magnification, and better ergonomics for the operator. Due to the minimally invasive nature of the surgery, hospital stays for patients having undergone robotic surgery are also shorter. Robotic surgery has an advantage over laparoscopic surgery, the other form of minimally invasive surgery, due to the aforementioned degree of motion of the robot “arm” and “wrist”. There is untapped potential for simulation of surgical procedures and techniques using surgical robotic systems. Finally, the global application/potential of these systems is just beginning to be imagined.
- Robotic assisted surgical systems have been used extensively in urology for prostate surgery, and, less commonly, in general surgery and most surgical subspecialties. Additional applications for these surgical-assist robots are continually being developed, the latest for ophthalmic/eye surgery.
- Disadvantages:
- The degree of training required, and the cost, especially since patient outcomes are, overall, similar to traditional surgery. Surgeons have some difficulty adjusting to the lack of tactile input from operating with these machines.
- Robot draw blood from a patient
- "Telemedical Network is Key in Accessibility " -Robotics in Healthcare
- InTouch Health in Action | InTouch Health's Telehealth Network
- With InTouch Health, patients in remote areas have access to high-quality emergency consultations for stroke, cardiovascular, and burn services. On the patient’s side it can be accessed on a tablet or personal computer, and clinicians can also use the same type of devices as best suits their needs.
- Bestic, the assistive eating robotic device
- Developed in 2004 by Sten Hemmingsson who had suffered a crippling paralysis from polio. The device is designed to lift food from the plate to the mouth, and is controllable of the user by touch of a button.
- The “Sedasys” System – Anesthesia (Mayo's article)
- It's a robotic machine that delivers anesthesia without an anesthesiologist. It has been developed for use in clinical settings and routine procedures such as colonoscopy and endoscopy. The rollout, by Johnson and Johnson, has been slow and the system is only used in four medical centers at this time, as the acceptance rate has been low due to fears regarding completely autonomous medical care .
 |
| The end of the robotic arm contains surgical instruments. It is crafted to mimic “human-like” wrist motion. – Da Vinci System (Picture from Mayo Clinic's article "Robots/Robotics in Healthcare") |
Non-clinical Application Rehabilitation Therapy
- Today, robots are capable of not only surgery, but also various other jobs in the field of health care, such as rehabilitating patients, providing/supporting professional care, and providing diagnostic assistance.
- The "Paro" seal robot
- This robot is intended to improve the health of the user by providing
him/her with social interaction. Paro shows how increased social contact and networking affects the recovery cycle and psychological stability of humans. - The robot was inspired from the fact that interacting with animals is emotionally
beneficial to mankind. The influence of social engagement on cognitive decline, particularly among elderly people, has been examined [65]. Paro is intended to counter the degenerative effects of lacking social interaction. The first interesting attribute of this robot is appearance. To make the robot seem inviting and friendly, the developers of the robot decided to model it after a baby harp seal covered with pure white fur. Paro contains tactile receptors under its “skin” capable of recognizing and measuring physical contact. The appearance of Paro can have a very positive effect on the acceptance of the robot by the users, particularly children and elderly who don’t require highly technical functionality [66], [67]. This 2.8kg (6.17lb) seal robot has four primary senses: sight (light sensor), hearing (voice recognition system with direction determination), balance, and tactile. - Paro is a good example of how software can provide significant functionality with
limited sensing and actuating components - Building off the topic on "Paro", in the article Robots Will Aid in Health Care as Population Ages, the author referenced a speaker at a RoboBusiness Conference in Boston, who said : "the medical needs of the aging adult population will increase the market for robotics to assist them in health care. And Japan is one of the countries that are facing the crisis of low fertility rate, and growing numbers of elderly, thus scientists, researchers and healthcare technologists would try to depend on A.I robotics to help solve certain diseases.
- The Dali walker or c-walker is a current project of the European Union and the Seimans Corporation

"The Dali walker is a programmable walker with multiple digital sensing devices for use in individuals with memory loss, dementia. The sensor system allows the walker to perceive and interpret its spatial environment in real time. By its navigational capabilities, this technologically advanced walker is mentally functioning for as well as affording physical support. This potent combination of both physical and mental assistance is potentially invaluable to an elderly person, who may have become timid about venturing out alone, especially in crowded or unfamiliar public places." (Mayo Clinic's article "Robots/Robotics in Healthcare")
Preventive Therapies and Diagnosis-Intelligent Fitness System
- Preventive therapies and diagnosis covers independent diagnostic methods such as robotized endoscope and teleoperation systems which independently monitor patients and preventive technologies such as intelligent fitness system and multiple objects motion/sound recognition system.
Robotic Assistance Technology-Intelligent Prosthetics
- Robotized assistance, such as intelligent prosthetics, robotized transportation system and manipulation assistances, is another important field of health care.
- An example will be the robotized artificial ankle shown in the figure above. This mechanical ankle senses which phase of stride the ankle is on, and manipulates
the angle of the bottom plates with springs. The stored energy in the spring releases to the next phase of walking which saves between 14 and 23% of the energy spent using conventional prosthesis. - Robot Suits and Exoskeletons: Musculoskeletal and Muscular Assistive Devices (Mayo's article "Robots/Robotics in Healthcare")











Get inspired by your blog. Keep doing like this
ReplyDeleteMMT Sharjah